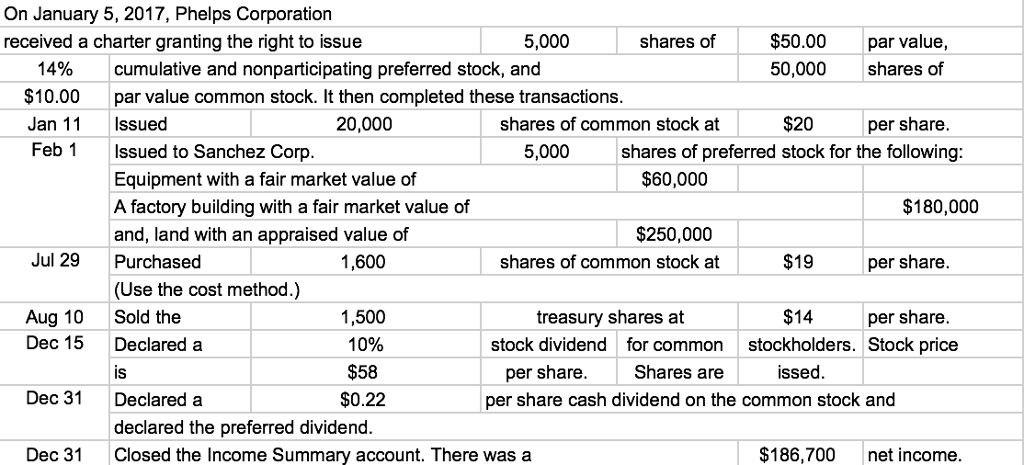
Although not mentioned directly, Kellogg now has only 382 million shares of common stock outstanding in the hands of the stockholders (419 million issued less 37 million treasury shares). This number is important because it serves as the basis for dividend payments as well as any votes taken of the stockholders. There are three types of transactions you will need to know when preparing a journal entry for common stock. These are issuing stock exchange for cash, for other non-cash assets or companies buying back their own stock. The $5,000 of the common stock account in the journal entry comes from the 5,000 shares multiplying with the $1 per share of the par value.
Recording Common Stock Issued Step-by-Step
Issuing common stock in exchange for a capital contribution has the advantage that unlike a loan, the business doesn’t have to pay back an equity investment. However, the investor who buys the stock has an ownership interest in the company, and the company has to make proper accounting entries in order to reflect the new capital contribution. The Common Stock account should be debited for the amount of money received from issuing the shares of common stock, while the Cash account should be credited for the same amount. The common stock also comes with the right to receive a part of the underlying company’s assets if it liquidates. Shareholders can only get access to those assets if the residual resources exceed the company’s liabilities. On top of that, preferred shareholders will get a preference during the distribution of the remaining assets.
Journal entries for the issuance of common shares
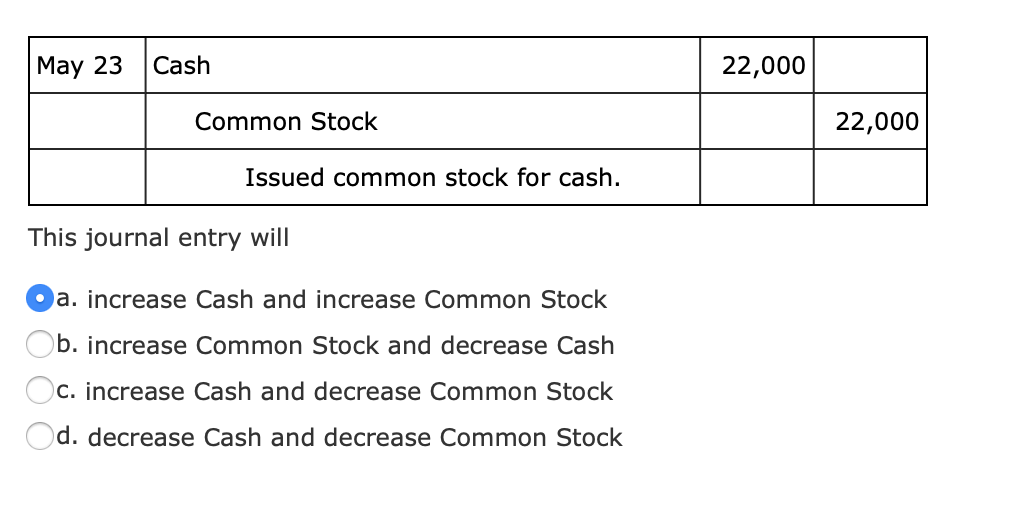
Most of the time, company issue the common stock for cash and use it for other purposes. Investors simply purchase the stock from the issuer and gain ownership over the company’s share. 5As mentioned earlier, the issuance of capital stock is not viewed as a trade by the corporation because it merely increases the number of capital shares outstanding.
Example of issuing common stock for cash
The building has a book value of $ 1.3 million but the owner claims that the fair value of the building is $ 1.5 million which base on the internal evaluation team. Company P share is trading at $ 100 per share in the capital market. 3A few states allow companies to issue stock without a par value.
The share buyback will retain in the company for a future issues, employee compensation, or retirement. 4As mentioned in the previous chapter, the sales of capital stock that occur on the New York Stock top 4 red flags that trigger an irs audit Exchange or other stock markets are between investors and have no direct effect on the company. Kellogg records the issuance of a share of $0.25 par value common stock for $46 in cash as follows3.
This account is also often called a Share Premium account, so you may see that in an exam. The debit to the bank account reflects the additional cash ABC now has from the share offering. The credit entry to the Class A Share Application reflects the liability the company also holds. And as we’ll see, some people will be getting their money back. The first example we will go through is the sale of common stock by ABC Ltd for cash. For example, on July 1, we issue 1,000 shares of common stock at the value of $15 per share.
In that situation, the entire amount received is entered in the common stock account. The debit to the allotment account creates monies that are now due to ABC Ltd. The credit to the share capital account and the additional paid-in capital reflects where is money is coming from, i.e. from people investing equity into the company. When a company issues new common shares from treasury, it means that the company is creating and selling new shares that have not previously been outstanding.
- “Issue” means to sell the shares of stock for the first time.
- It has nothing to do with the market price of the company share.
- When it issues no-par stock with a stated value, a company carries the shares in the capital stock account at the stated value.
- The first example we will go through is the sale of common stock by ABC Ltd for cash.
- However, the transaction amount depends on assets market value or common stock market value whichever can be measured more reliability.
- Likewise, we need to make the journal entry for issuing the common stock in order to account for the increase in the capital section of the equity on the balance sheet.
After buying back Kevin’s shares, ABC decides to retire the shares on July 31. After Board approval, ABC’s accounts team would prepare the following journal entry. Now we are into the exciting part of the article, the journal entries.
The company needs to reverse the treasury stock with common stock and additional paid-in capital. DeWitt carries the $ 30,000 received over and above the stated value of $200,000 permanently as paid-in capital because it is a part of the capital originally contributed by the stockholders. However, the legal capital of the DeWitt Corporation is $200,000. Traditionally, companies have gotten around this limitation by setting the par value at an extremely low number2.
Any remaining proceeds will increase the line item for additional paid-in capital in excess of par value. The differentiation between the two accounts depends on the share’s par value. Accounting standards require companies to recognize the finance received from issuing shares in the two accounts.